我院徐子晨教授团队泛在数据分析与优化实验室(GOODLab)近期在数据库测试领域取得了重要突破,其研究成果"SRS: Detecting Logic Bugs of Join Implementation in DBMSs via Set Relation Synthesis" 被国际数据管理顶级会议 SIGMOD 接收。SIGMOD 会议是数据库与数据管理领域最具影响力的三大国际会议之一,与 VLDB、ICDE 齐名,并获得中国计算机学会(CCF)A 类国际会议推荐。这一成就不仅是对 GOODLab 研究实力的高度认可,更是实验室成员赖锦辉及团队辛勤付出的结晶。
一、研究团队
作者:
Jinhui Lai, Nanchang University, China
Chi Zhang, Tsinghua University, China
Binyan Li, Nanchang University, China
Chengling Liang, Nanchang University, China
Jie Liang, Beihang University, China
Zhiyong Wu, Tsinghua University, China
Jingzhou Fu, Tsinghua University, China
Yu Jiang, Tsinghua University, China
Zichen Xu*, Nanchang University, China
指导教师:
徐子晨教授,南昌大学
姜宇副教授,清华大学
二、论文摘要
Logic bugs can cause DBMSs to silently produce incorrect results for a given query, posing significant threats to software reliability and remaining challenging to detect. Join is a fundamental operation in DBMSs, enabling the combination of data from multiple tables; however, due to its complexity, it is also susceptible to logic bugs. Existing works detect logic bugs in join optimizations by altering query hints and system variables to alter the optimizer’s choice of execution plans. However, these approaches struggle to detect logic bugs when query hints or system variables fail to influence the optimizer’s behavior, or when the logic bugs reside in join implementation code that is unrelated to optimization. In this paper, we present Set Relation Synthesis (SRS), a black-box testing approach that detects logic bugs of join implementation in DBMSs by leveraging set relations among different join operations. SRS applies transformations to the original join queries, including modifications to join types, join orders, and join conditions, while ensuring that the outputs of both the original and transformed queries preserve the expected set relations. Violations of these set relations indicate potential logic bugs. We realized SRS and evaluated it on five widely-used and extensively-tested DBMSs: MySQL, MariaDB, TiDB, PostgreSQL, and DuckDB. SRS uncovered 36 previously unknown and unique bugs, all of which have been confirmed, with 12 already fixed. Among these, 33 are logic bugs, demonstrating SRS’s effectiveness and practicality in detecting logic bugs in the implementation of join operations within DBMSs.
三、研究背景
Join 是数据库中最常用且最复杂的算子之一,它负责将多张表中的数据关联起来,生成新的结果集。由于 Join 操作涉及多种实现方式(如嵌套循环连接、哈希连接、排序合并连接等)以及各种边界条件和特殊情况处理,其代码量庞大且复杂度极高。
过去,检测 Join 实现中的逻辑缺陷主要依靠“换计划”的方法——通过添加查询提示(hint)或修改系统参数,使优化器选择不同的执行路径。尽管这种方法在某些情况下能够发现逻辑错误,但它存在明显的局限性。当逻辑缺陷隐藏在执行器层面(例如哈希表去重、空值拼接等),而不是优化器的选择过程中时,现有方法往往无能为力。
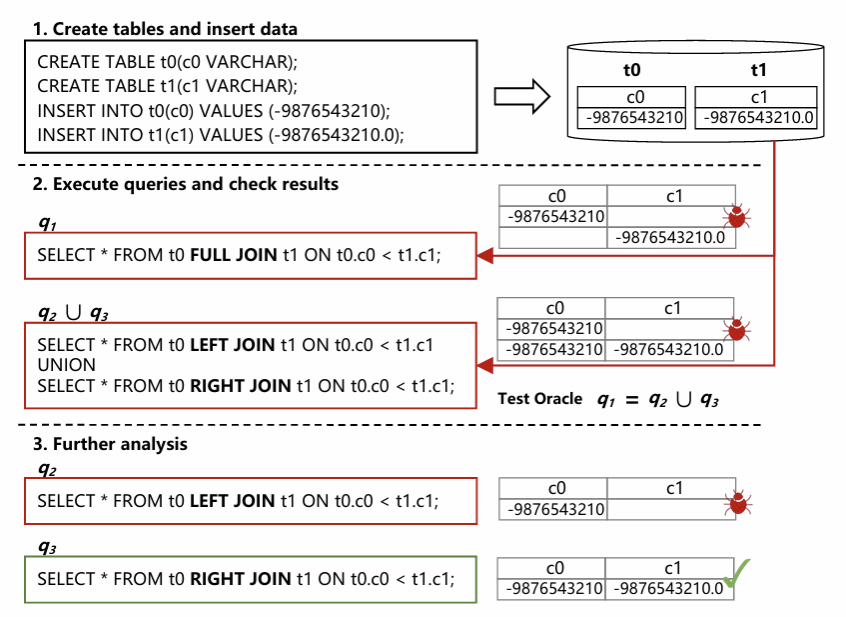
四、研究概述
针对上述问题,本研究提出了一种基于集合关系合成的逻辑缺陷检测方法 SRS。该方法通过利用不同 Join 操作之间的集合关系,系统性地检测 DBMS 中 Join 实现的逻辑缺陷。具体而言,SRS 首先随机生成一个包含 Join 操作的原始查询;随后,基于论文所提出的集合关系模型,生成与原始查询具有特定集合关系的转换查询;最终,通过检验原始查询与转换查询的结果是否满足预定义的集合关系,判断 Join 实现是否正确。任何违背预定义集合关系的结果,均表明目标 DBMS 中可能存在 Join 相关的逻辑缺陷。
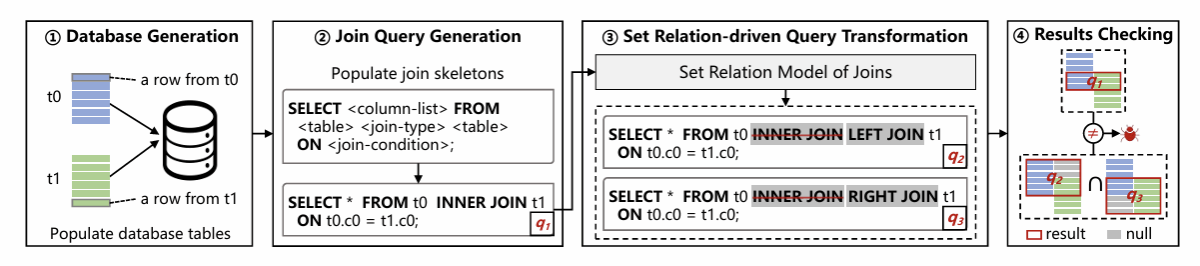
五、研究成果
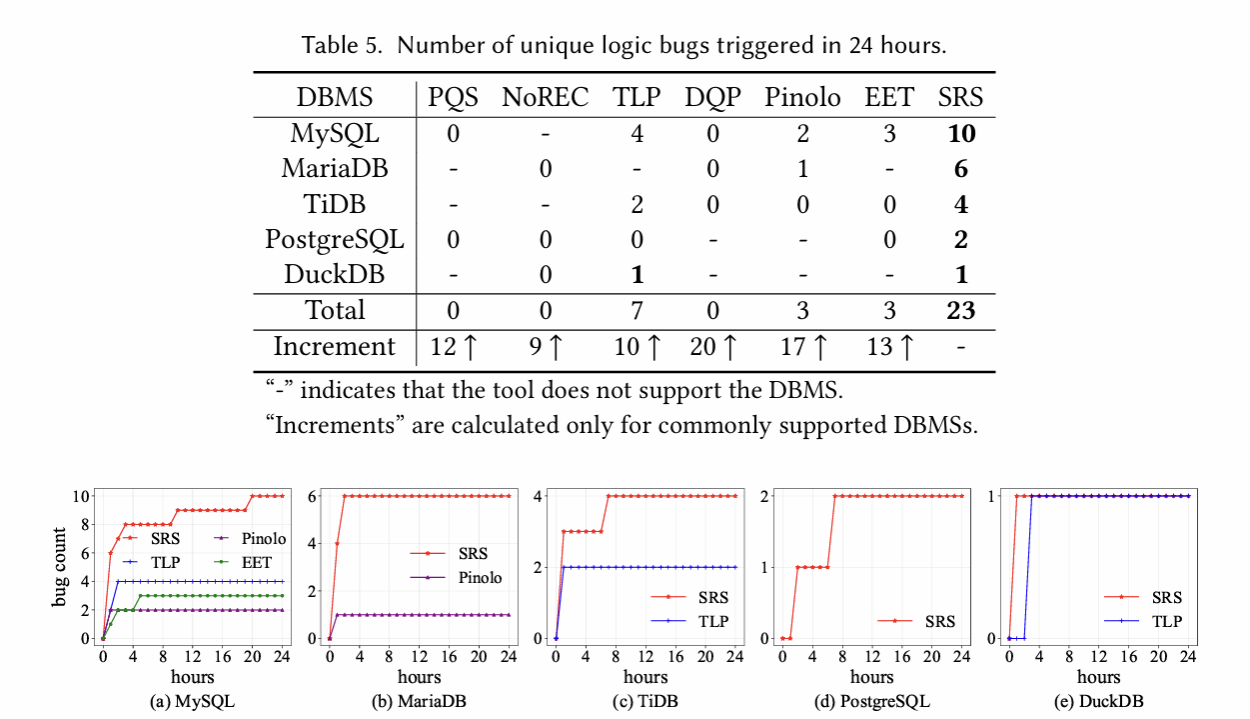
SRS 方法在实际应用中展现出了强大的威力。在 MySQL, MariaDB, TiDB, PostgreSQL, DuckDB 等五个主流数据库管理系统中,成功检测出 36 个未知缺陷,为数据库的稳定运行提供了有力保障。
这些未知缺陷的发现,不仅体现了 SRS 方法的有效性和准确性,更具有广泛的工程应用前景与实践价值。未来,该方法有望应用于更多的数据库系统,为数据管理领域带来新的变革。
此次研究成果的成功发表,是对赖锦辉同学及其团队辛勤工作的认可。赖锦辉在工作中的卓越表现,不仅彰显了他的科研能力和创新精神,也为 GOODLab 在数据库测试领域的研究树立了新的标杆。
未来,GOODLab将继续深耕数据库与数据管理领域,探索更多前沿技术,解决更多实际问题。我们期待与更多学术界和工业界的同仁们携手合作,共同推动数据库技术的发展,为构建更加可靠、高效的数据管理系统贡献力量。
阅读延伸
论文PDF链接:
http://wingtecher.com/themes/WingTecherResearch/assets/papers/paper_from_25/srs_sigmod25.pdf
ACM Reference Format:
Jinhui Lai, Chi Zhang, Binyan Li, Chengling Liang, Jie Liang, Zhiyong Wu, Jingzhou Fu, Yu Jiang, and Zichen Xu. 2025. SRS: Detecting Logic Bugs of Join Implementation in DBMSs via Set Relation Synthesis. Proc. ACM Manag. Data 3, 6 (SIGMOD), Article 363 (December2025),24pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3769828
